化学
Computation in 化学
从历史上看, chemistry was understood as being organized into two broad categories: experimental and computational. 然而, that classification system has become increasingly inadequate to describe the fascinating and diverse types of chemistry research now available due to increased computing capabilities. 例如, computational models can help us estimate how molecules fit into enzymes to control their expression, so we can maximize the time and materials devoted to drug discovery. 同样的, innovative methodology like leaf spray ionization rapidly develops massive data sets as we endeavor to understand plants’ intricate response to predators. 此外, harnessing the computing power of supercomputers enables physical chemists to elucidate the vibrational modes in crystal structures. 因此, for these and many other chemistry applications, it is vital to develop the knowledge, 技能, and experience for students to learn computations 技能 to work on modern, complex chemical studies.
 Phil Wittel presenting at Eli Lilly & Company
Phil Wittel presenting at Eli Lilly & Company
 Phil Wittel presenting at the Butler Undergraduate Research Conference
Phil Wittel presenting at the Butler Undergraduate Research Conference
Questions addressed by computers in chemistry
How do intermolecular forces determine how small molecules with various side chains fit into the active site of an enzyme or DNA?
How does the age of a plant and the location of a leaf affect how rapidly can a plant produce and expel molecules to deter predators from consuming them?
Computation in 化学 and Biochemistry at UE
The curriculum in the Department of 化学 at UE is designed to prepare students for a variety of satisfying and meaningful careers. Our students begin contributing to the scientific community as undergraduate researchers, then continue on to careers in industry, 研究生学位, 或者职业学校. Our dedicated faculty mentor students in undergraduate research in a diverse variety of computational-based projects.
The Lampkins Supramolecular 化学 Lab uses a program called Autodock Vina to virtually test compounds that we design to inhibit the replication of gram-negative, drug resistant bacteria.
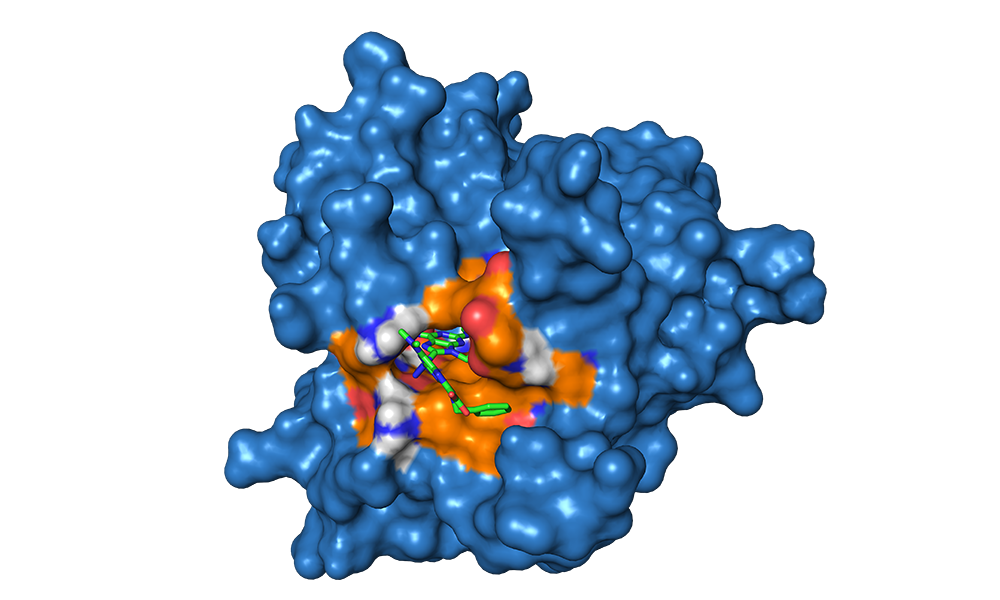
Target compound in the ATP-binding site of E. 杆菌 gyrase B using Autodock Vina
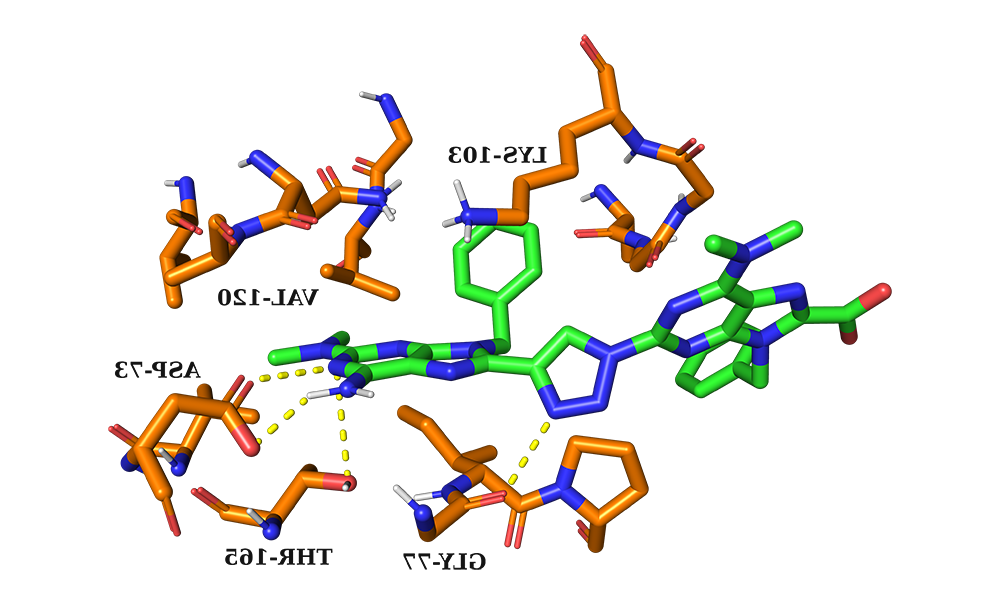
The binding mode of the target compound in the ATP binding site of E.杆菌 gyrase B using Autodock Vina
Dr. Lampkins obtained grant funding and mentored Phil Wittel, who performed a computational chemistry visualization project in which he modeled potential target molecules for their fit in the ATP binding site of E. 杆菌 gyrase B in AutoDock Vina. The results then informed the selection of molecule targets for organic chemistry undergraduate research also being pursued in the group.
Dr. Lynch obtained funding from the National Science Foundation (NSF) XSEDE program to utilize time on the supercomputer Stampede to study vibrations in crystals of cyclopentane.
办公室电话
812-488-2029
办公室的电子邮件
cism@kanaryasevenler.net
办公室的位置
Room 216, Koch Center for Engineering and Science
